Research
Project
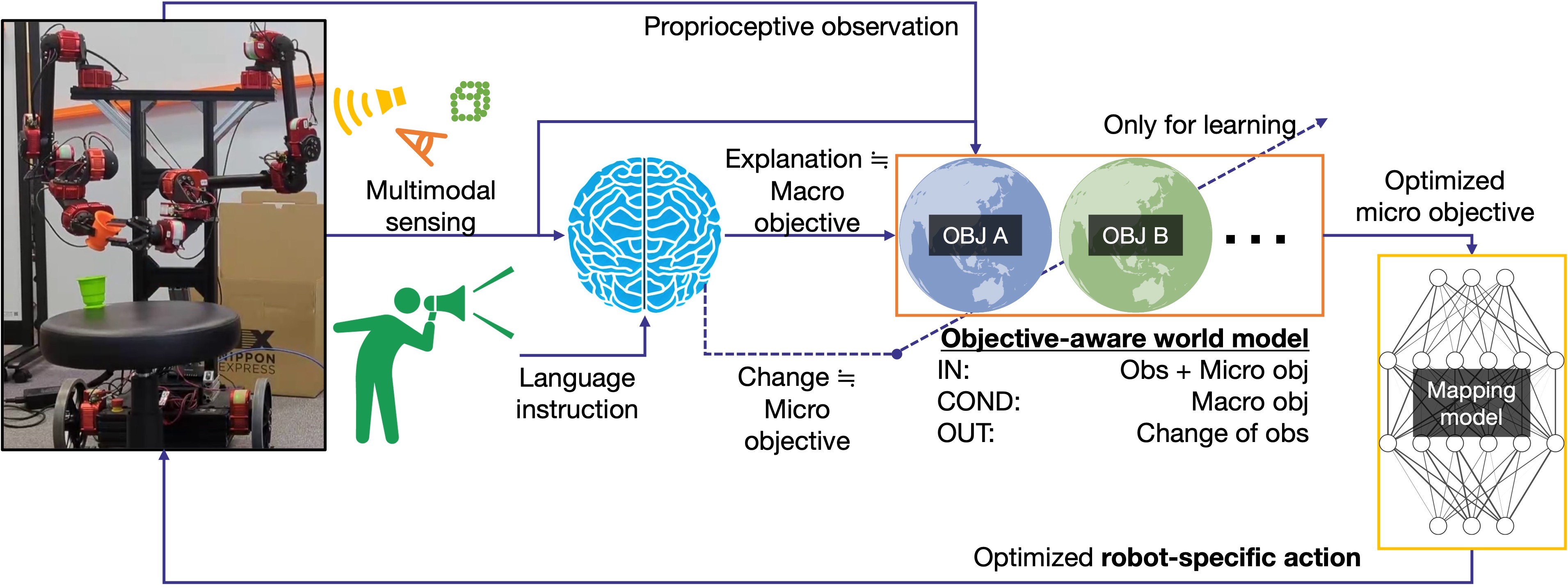
Inclusive robotic foundation model (JST CRONOS)
We develop a world model connected to a foundation model that can optimize the actions for various robots in response to language instrutions.- Mapping between latent action space common among robots and robot-specific action spaces
- Lightweight hypernetworks that switch internal state representation according to language instrutions
- Learning world model interpreted as multi-objective optimization
Reinforcement learning
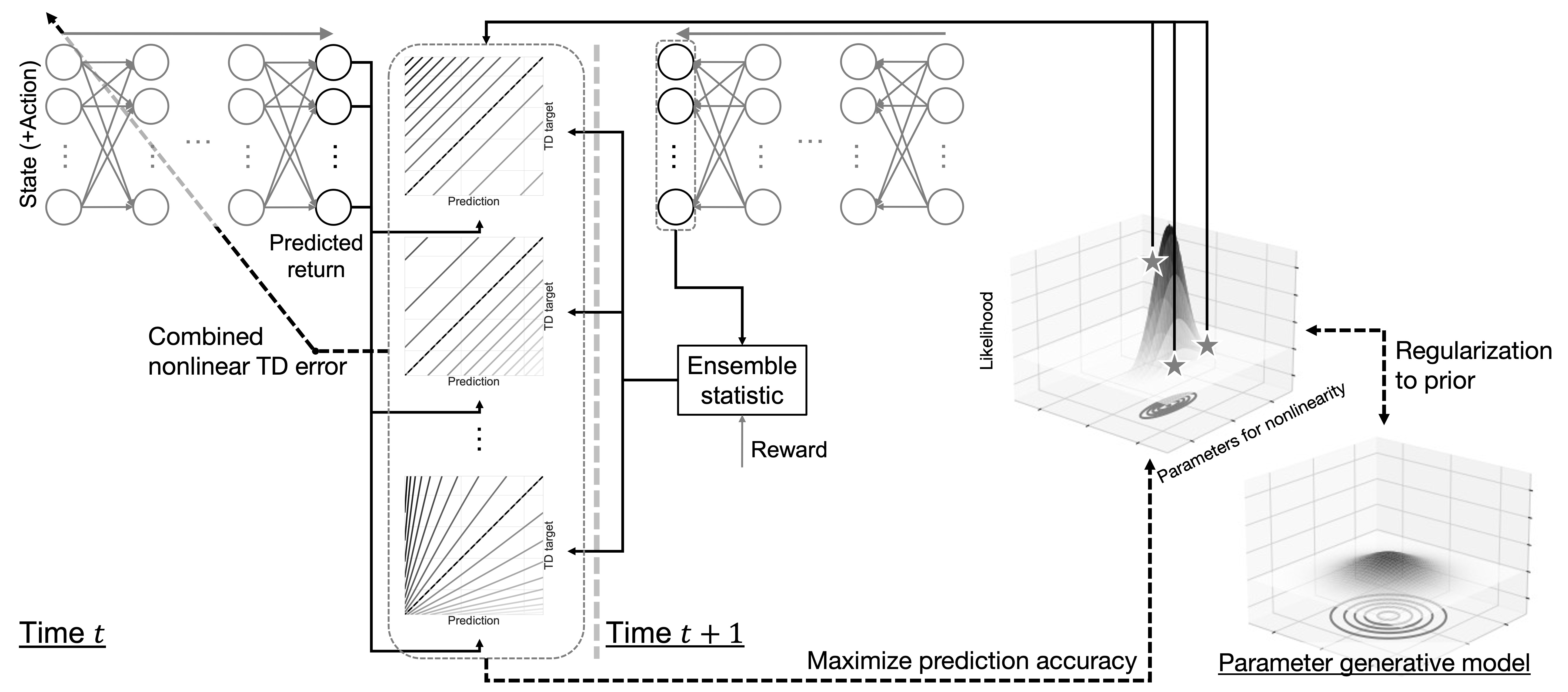
Reinforcement learning as probabilistic inference
We derive and analyze various values that can be found by interpreting RL as a kind of probabilistic inference problem.- Optimization of discount factor according to events
- Weber-Fechner law in TD learning
- Distributional model with regular optimism and pessimism
- Theoretically-grounded optimistic learning
- Integration with feedback error learning
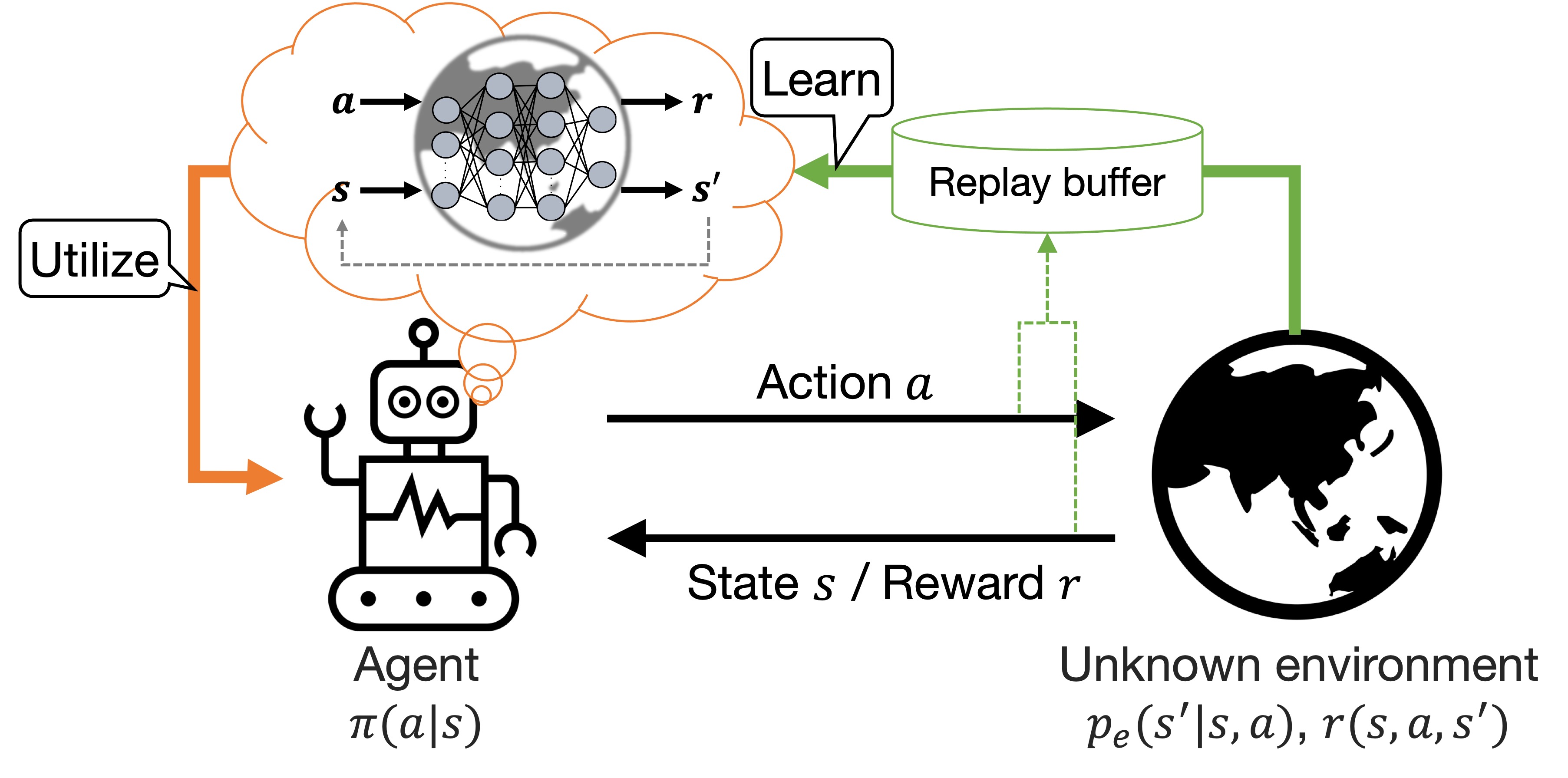
Model-based reinforcement learning
We study learning theory of world model and its application to model predictive control in real time.- Integration of model predictive control, imitation learning, and reinforcement learning
- Adversarial learning with moderate robustness and less conservativeness
- Model predictive control with efficient convergence to a suboptimal solution
- Extraction of sparse low-dimensional latent space
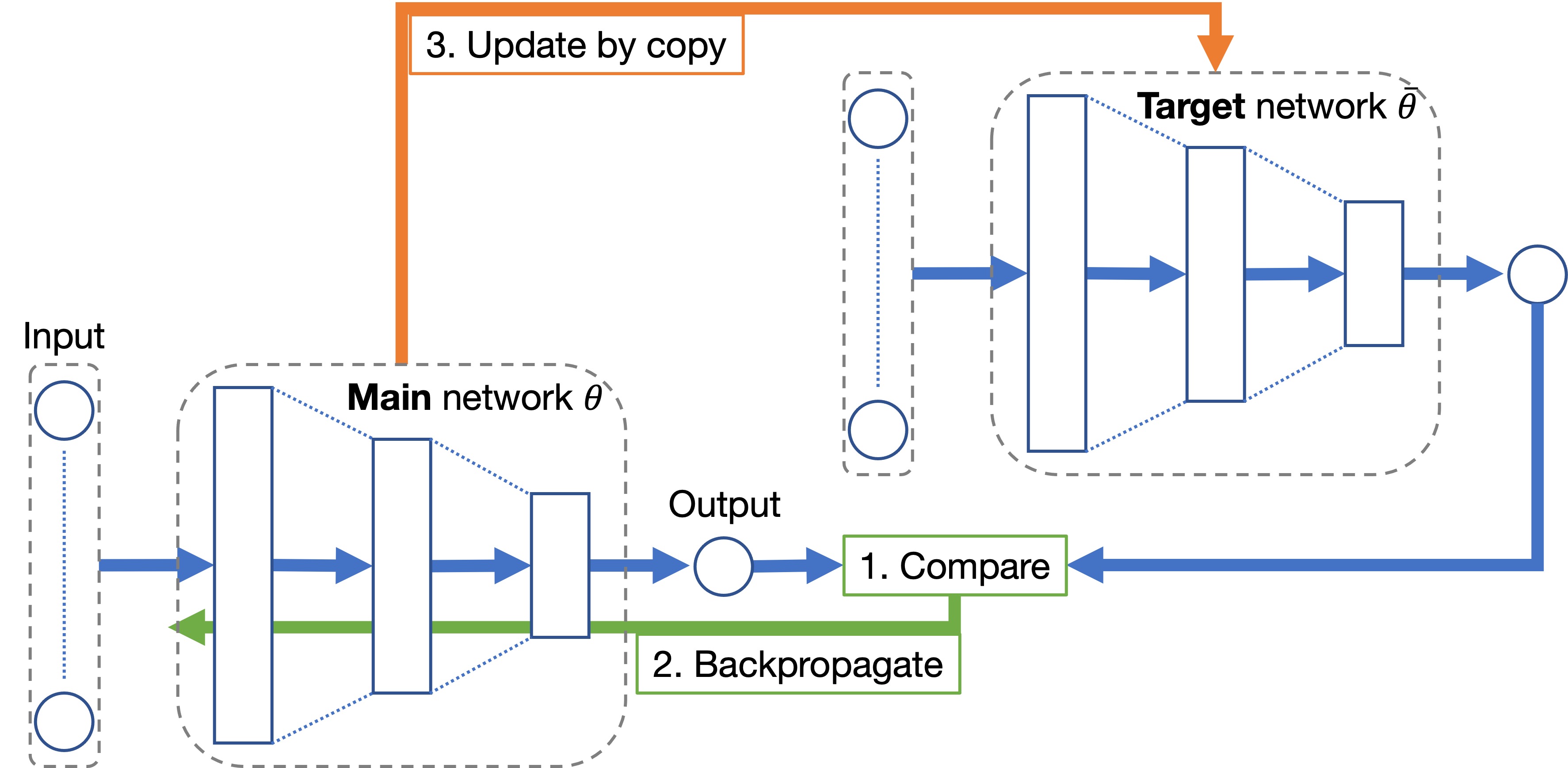
Stabilization of deep reinforcement learning
We develop stabilization techniques that enable deep reinforcement learning to optimize policies stably.- Optimization of divergence direction in policy improvement
- Analysis of experience replayable conditions
- Stable and fast target network updates
- Regularization of local Lipschitz continuity of policy and value functions
Imitation learning
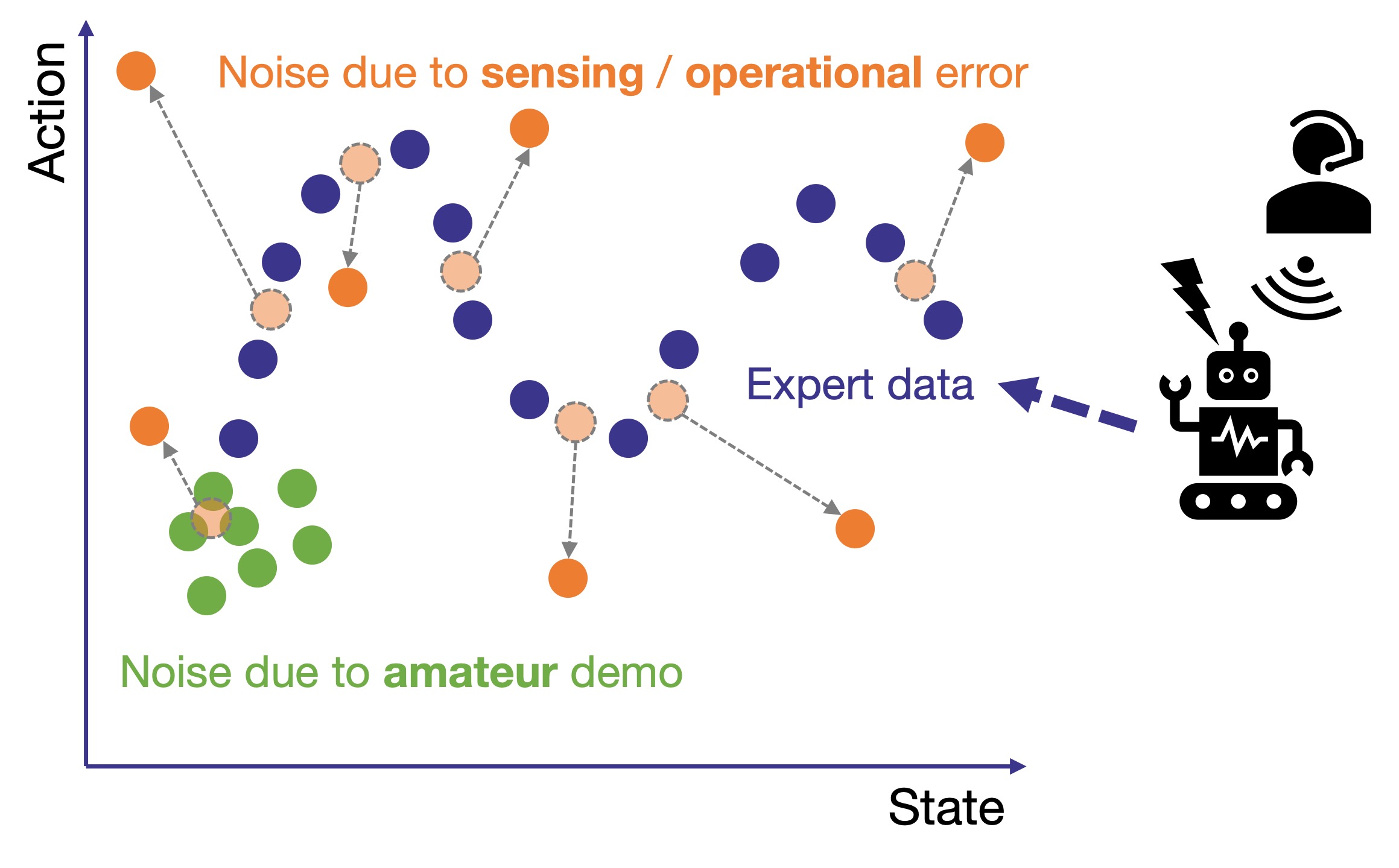
Utilization of imperfect demonstration
We develop imitation learning methodologies in the absence of sufficient quality, modality, and quantity of demonstration data.- Guided reinforcement learning with rough target trajectories as constraints
- Spatiotemporal partial imitation through self-paced learning
- Robust behavioral cloning for outliers based on Tsallis statistics
- Safe and efficient framework to compensate for missing action data
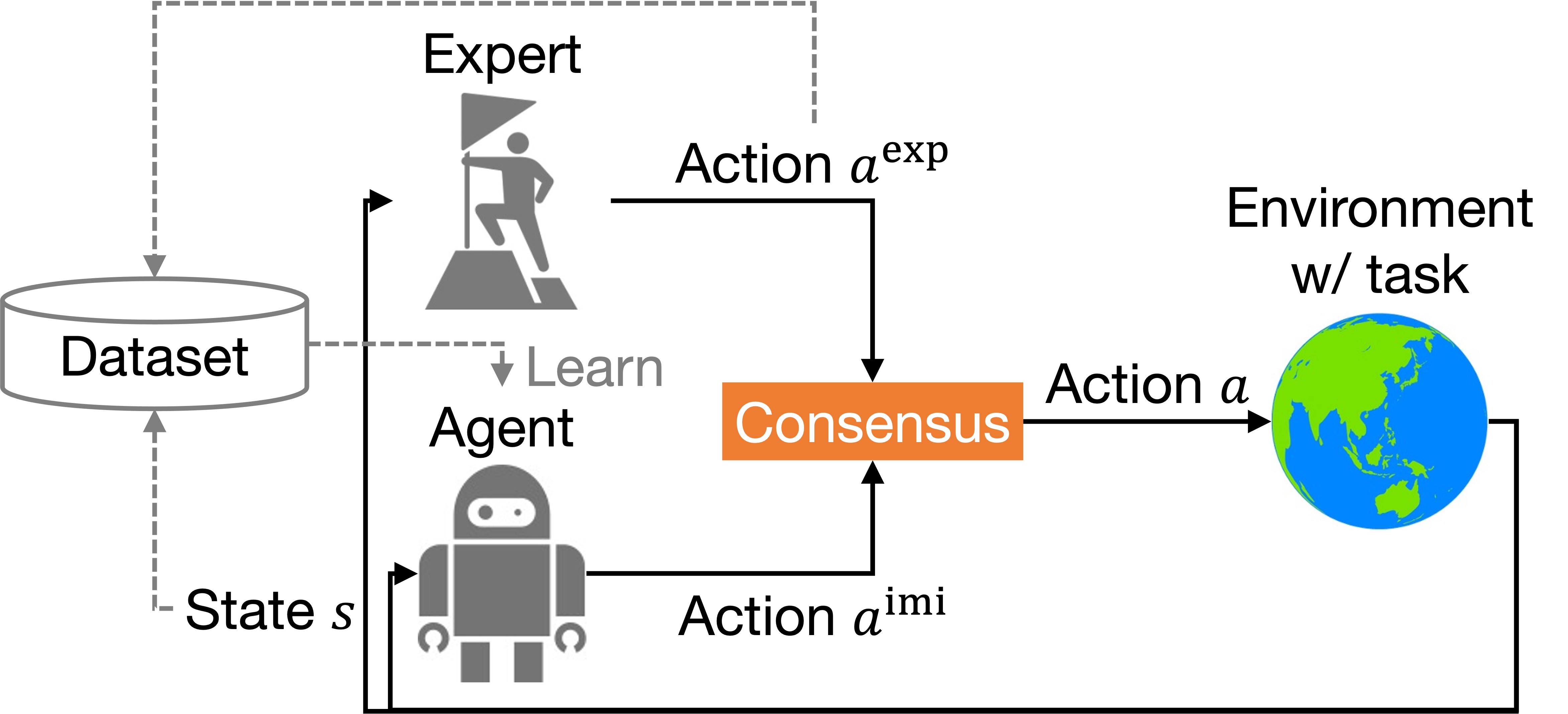
Interactive imitation learning
We study a framework in which the demonstrator and agent collaborate to collect data to be imitated.- Lifelong learning of non-stationary multiple tasks
- Active exploration without sacrificing the sense of agency
- Optimal consensus decision-making among multiple actions with confidences
Other machine leanring
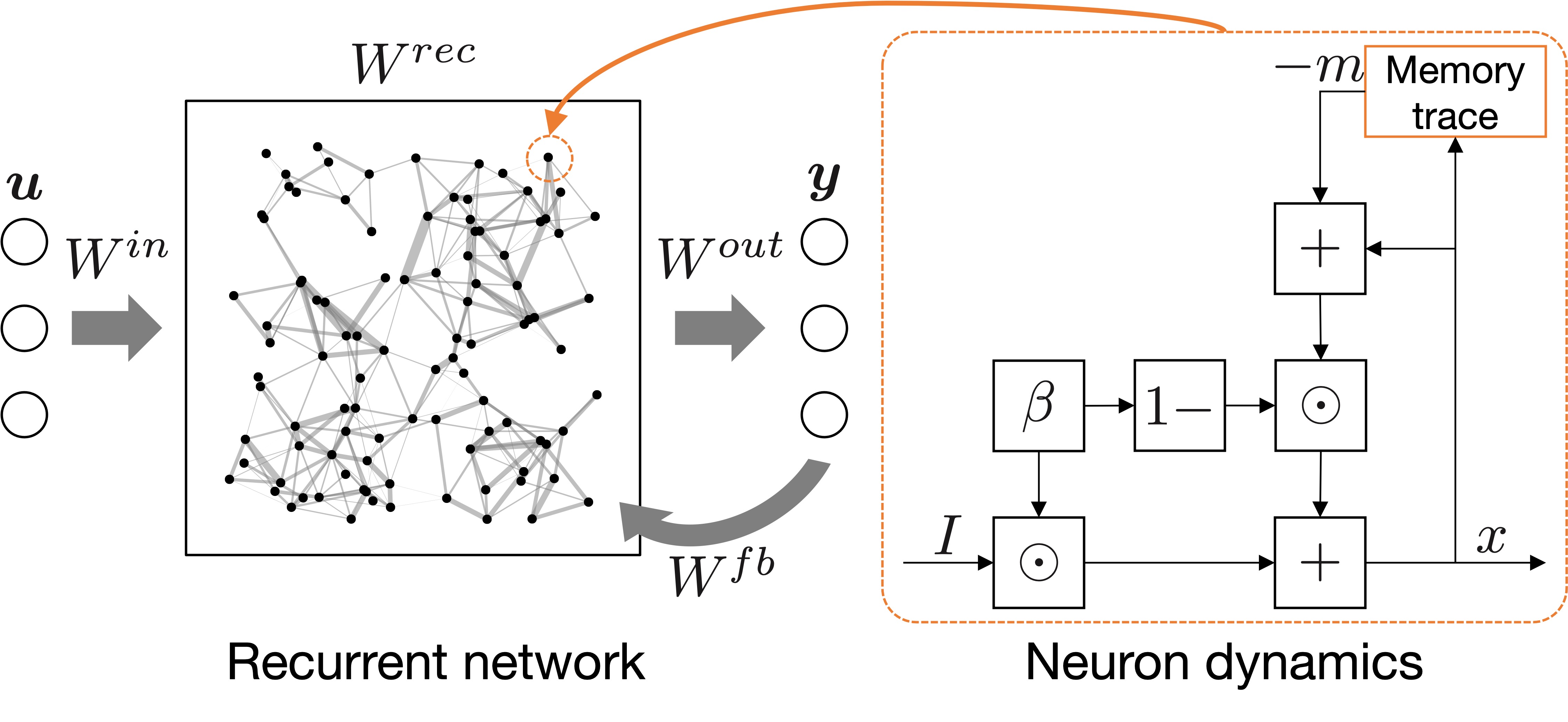
Time-series data processing
We design models to process time-series data, which is important for analyzing and representing robot and human motions.- Learning theory of recurrent neural networks based on variational inference
- Design of reservoir computing in complex domain that embeds the representation of periodicity
- Approximated implementation of neuron dynamics following a power law
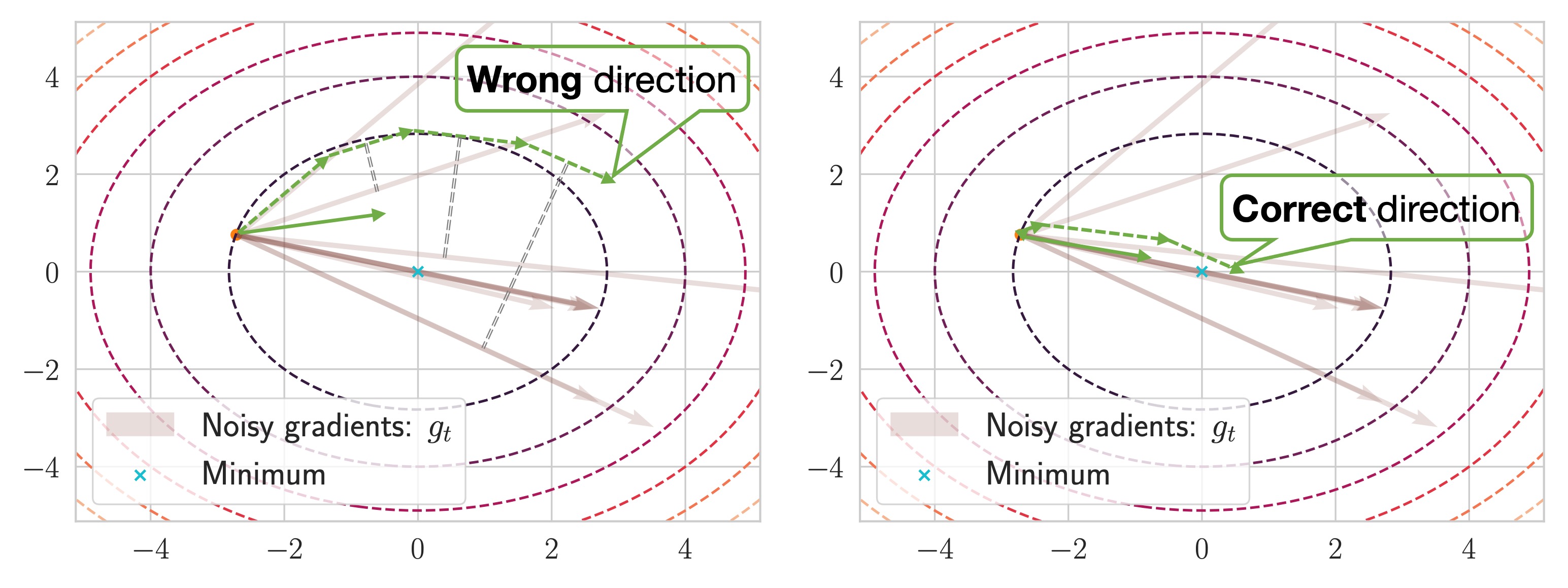
Stochastic gradient descent
We improve the performance of the stochastic gradient descent, which is a core technique in deep learning.- Novel interpretation of Lookahead optimizer
- Robustness to noise and outliers based on Student's t-distribution
- Improvement of AMSGrad to make it applicable to non-stationary problems
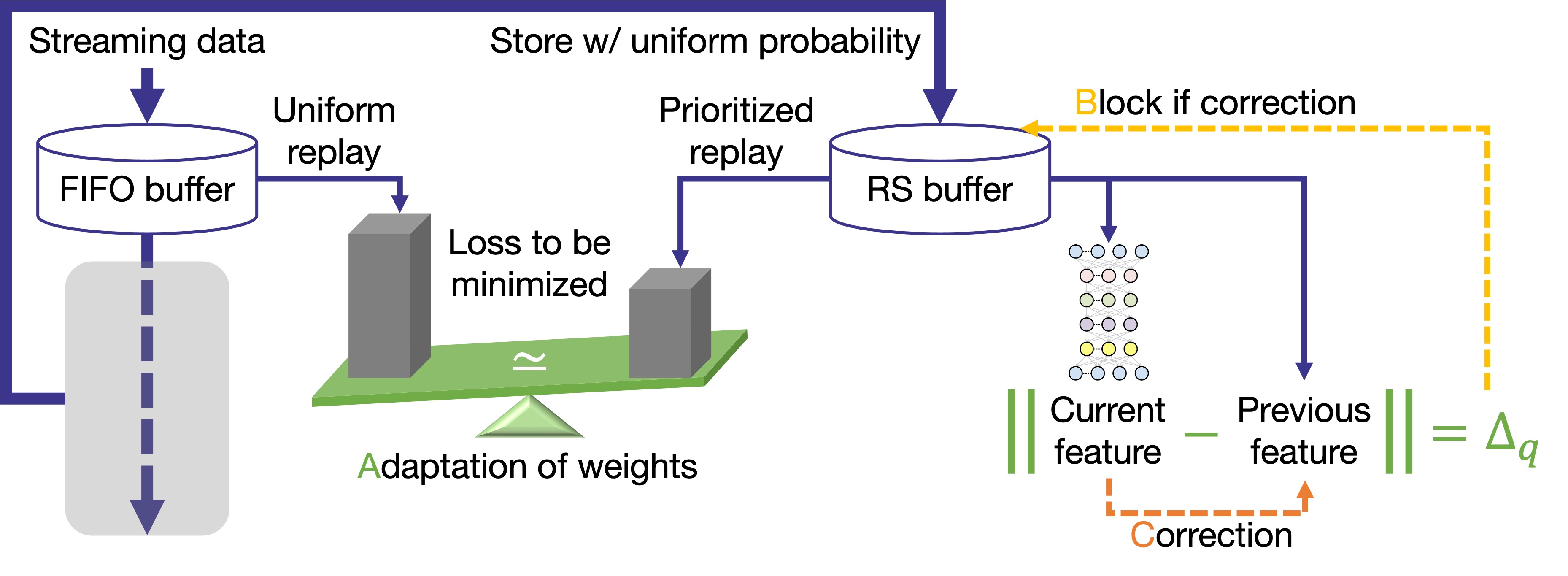
Lifelong (continual) learning
We develop fundamental technologies for autonomous robots to keep learning continuously.- Stochastic gradient descent without catastrophic forgetting
- Generalization and hierarchization of reservoir sampling
- Optimization of balancing rehearsal and function regularization
- Fractal model for continual learning of multiple tasks
Domain-oriented
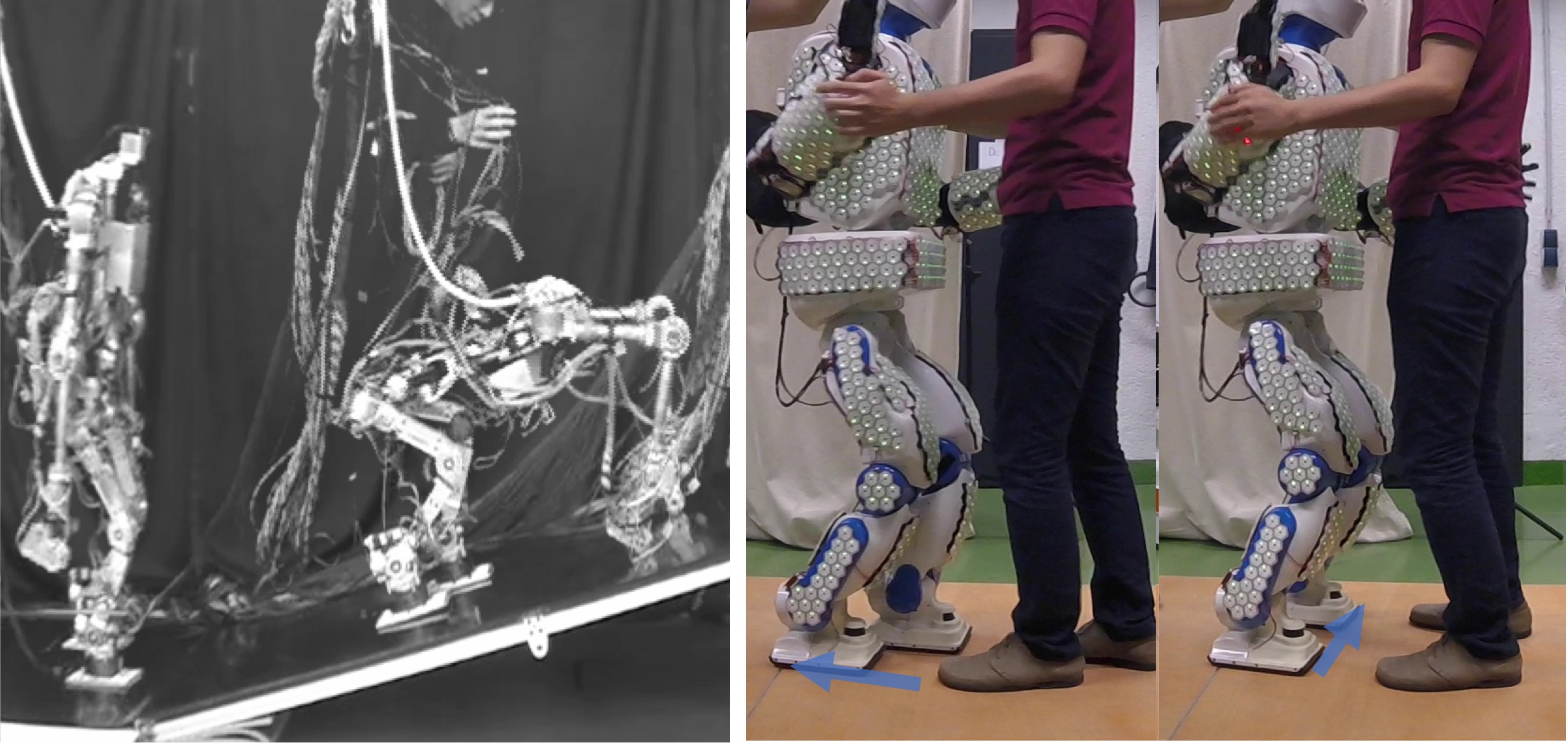
Humanoid robots
We study motion control of humanoid robots, which are expected to play an active role in human society as general-purpose robots.- Integration of whole-body model predictive control and machine learning
- Dancing with a partner using whole-body skin sensors
- Unified controller for bipedal walking and running and continuous transition between them
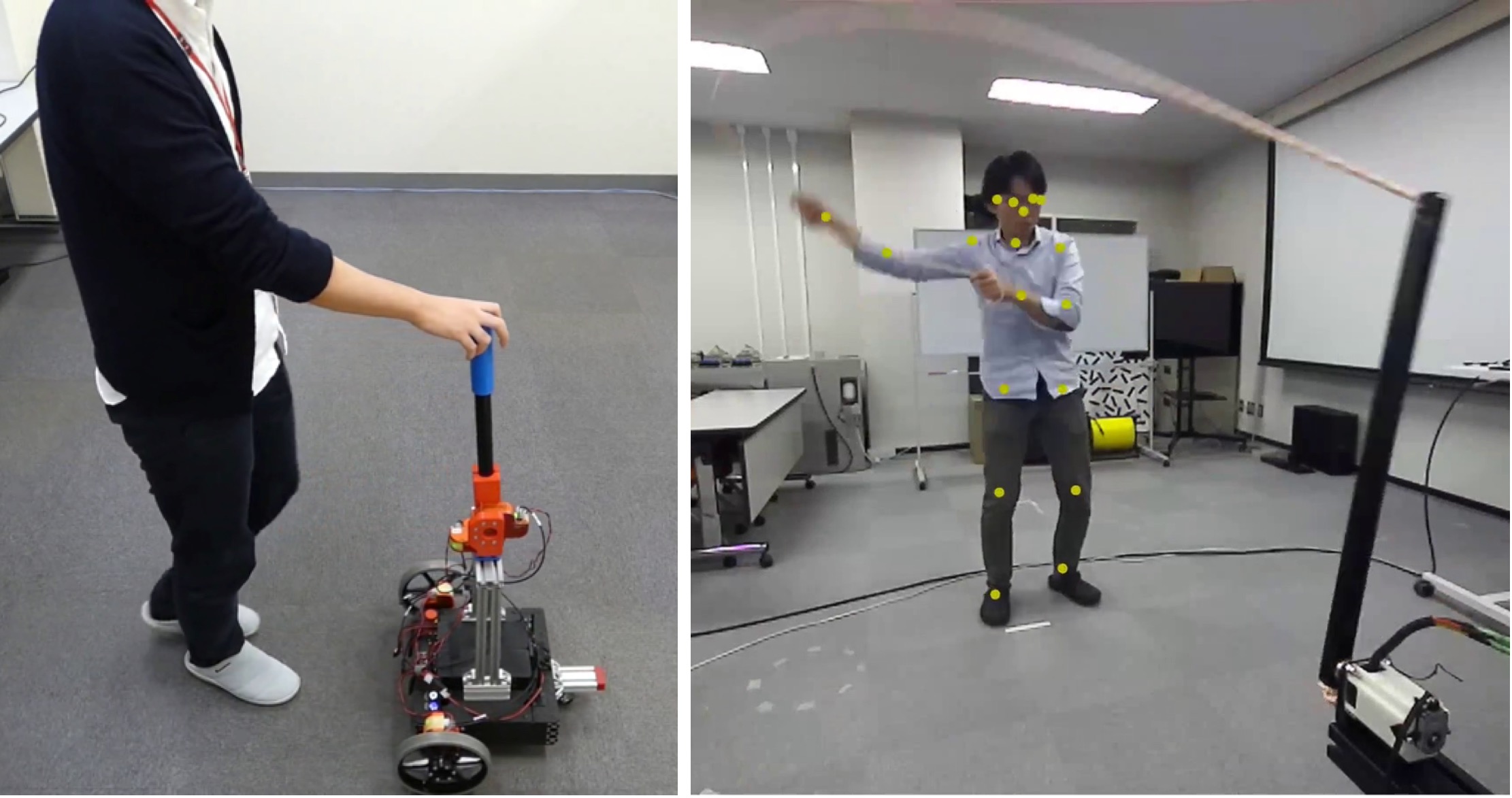
Human assistive robot
We develop AI technologies to assist various people.- Extracting and understanding the tacit knowledge hidden in subjective evaluation
- Surgical assistance with learning-based model predictive control
- Learning assistance in embryo manipulation with extracted expert skills
- Locomotion assistance based on recognition of human movement behaviors